Chinese Pronunciation Tips: How to Master Mandarin Sounds Correctly
Chinese Pronunciation Tips: How to Master Mandarin Sounds Correctly Chinese pronunciation, especially Mandarin, is vital for clear communication—its tonal system and unique phonetics often challenge learners. However, with targeted methods, anyone can improve accuracy. First, master Pinyin fundamentals. Pinyin, Mandarin’s romanization system, breaks sounds into initials (e.g., “b,” “zh”) and finals (e.g., “a,” “ing”). Focus on distinguishing easily confused pairs like “b/p” (unaspirated vs. aspirated) or “s/sh” (flat vs. retroflex tongue). Use official guides or trusted apps to avoid mislearning.
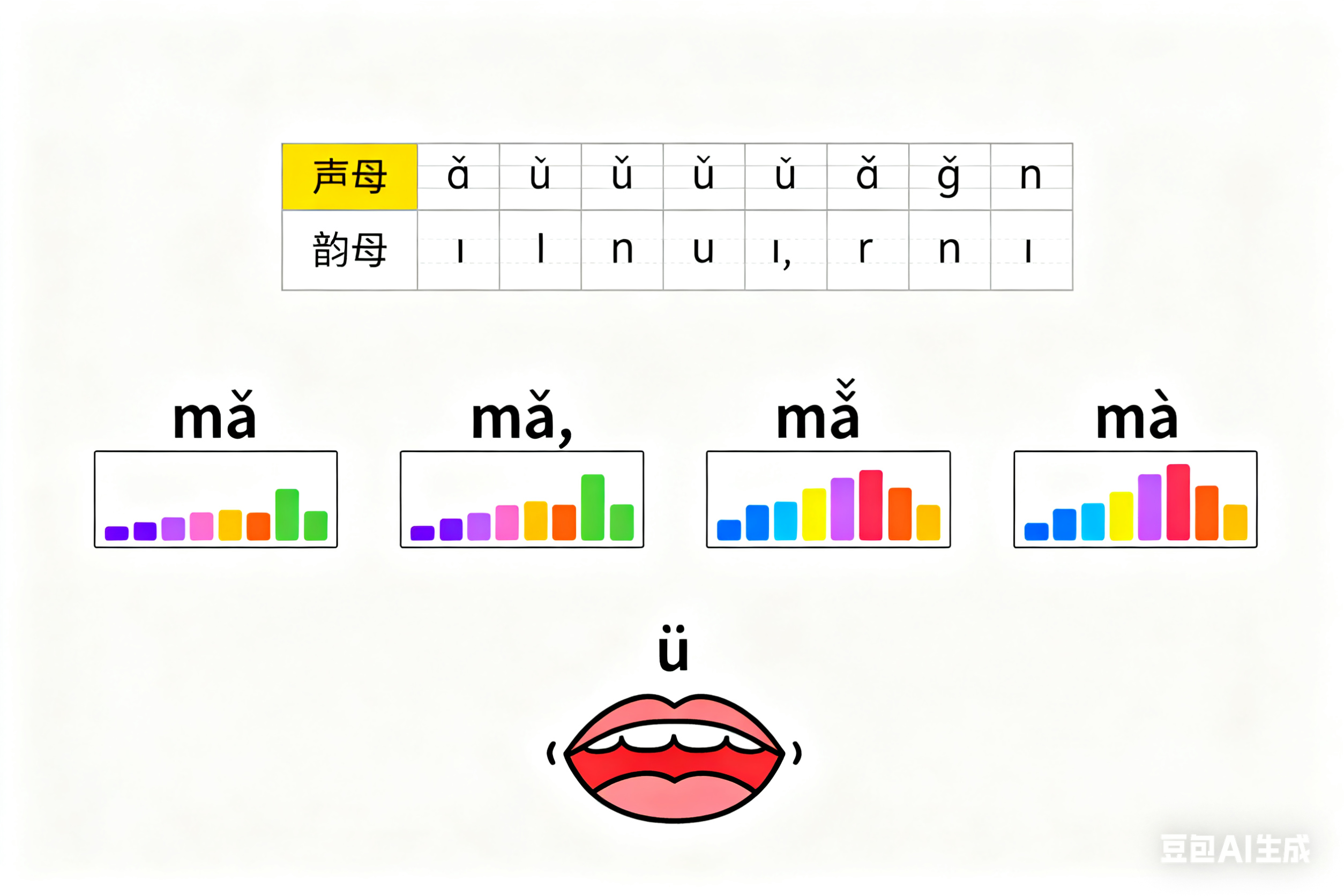
Second, prioritize tone practice. Mandarin has 4 core tones (plus neutral) that change word meaning—“mā” (mother) vs. “mǎ” (horse), for example. Practice tone contours slowly: use hand gestures (e.g., flat hand for tone 1, rising hand for tone 2) to reinforce pitch changes.
Third, mimic native speakers. Listen to short clips from Mandarin podcasts (e.g., Coffee Break Chinese) or shows, then repeat aloud. Pay attention to rhythm, not just individual sounds—native speakers often link syllables smoothly.
Finally, train mouth muscles. Sounds like “ü” (round lips) or “ch” (curled tongue tip) don’t exist in English. Do 5-minute daily drills: hold the “ü” sound for 3 seconds, or practice “zh/ch/sh” with words like “zhōngguó” (China).
Consistency beats perfection—15–20 minutes of daily practice will build muscle memory, making your Mandarin pronunciation clear and natural.
Please login to comment